
When discussing anti-aging supplements, the comparison of collagen vs glycine is quite common. Collagen helps your skin by making it stretchy and hydrated, while also reducing wrinkles. A study involving 85 women demonstrated improved skin moisture and firmness after two months of using collagen. On the other hand, glycine aids your body in self-repair. It supports the production of more collagen and maintains cell health. Both collagen and glycine work together to combat aging, but your choice between collagen vs glycine ultimately depends on your specific goals. Are you aiming for better skin or enhanced body repair?
Key Takeaways
Collagen helps skin stay stretchy and moist, reducing wrinkles.
Glycine helps make collagen and fixes cells, keeping skin healthy.
Taking collagen and glycine together boosts their anti-aging benefits for skin, hair, and joints.
Collagen supplements can work in 8-12 weeks, especially for skin moisture.
Glycine can help you sleep better, which helps your body heal.
Pick collagen types based on needs: Type I for skin, Type II for joints, and Type III for muscles.
Foods like bone broth and chicken skin have collagen. Meat and fish have glycine.
Talk to a doctor before trying new supplements to stay safe.
Collagen vs Glycine: Understanding the Basics
What Is Collagen?
Structure and Role in the Body
Collagen is the most common protein in your body. It makes up about 30% of all the protein in your body. It works like a framework, giving strength to your skin, bones, muscles, and tissues. Think of it as the “glue” that keeps everything together. Collagen is made from amino acids like glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. These amino acids form a special triple-helix shape, making collagen strong and stretchy.
This protein helps keep your skin stretchy, your joints healthy, and your tissues repaired. As you get older, your body makes less collagen. This can cause wrinkles, loose skin, and joint pain. Taking collagen supplements can help fight these problems and keep your body working well.
Natural Sources of Collagen
You can increase collagen by eating certain foods. Here are some examples:
Bone broth: Made from animal bones, it’s full of collagen.
Chicken skin and fish skin: These are high in collagen.
Egg whites: They have proline, which helps make collagen.
Citrus fruits and berries: They don’t have collagen but have vitamin C, which helps your body make it.
What Is Glycine?
Function as an Amino Acid
Glycine is the simplest amino acid, but it’s very important for your health. It helps build proteins, especially collagen, where it makes up about 35% of the amino acids. Its small size helps it fit into collagen’s triple-helix shape, keeping it strong and stable.
Glycine does more than just help collagen. It works in your brain to help with thinking and sleep. It also helps make glutathione, an antioxidant that protects your cells from damage.
Natural Sources of Glycine
You can find glycine in many foods, such as:
Meat and poultry: Beef, chicken, and pork are great sources.
Fish: Found mostly in the skin and bones.
Gelatin: A rich source of glycine made from collagen.
Legumes and seeds: Plant-based options like soybeans and sunflower seeds have glycine.
Key Differences Between Collagen and Glycine
Composition and Biological Functions
Collagen and glycine are different in what they are made of and how they work. Collagen is a complex protein made of several amino acids like glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. It gives strength and stretchiness to your tissues. Glycine is a single amino acid that helps build collagen and other proteins.
Here’s a simple comparison:
Feature | Collagen | Glycine |
|---|---|---|
Composition | Protein made of many amino acids | Simplest amino acid |
Primary Role | Gives strength and support | Helps build proteins |
Additional Functions | Keeps skin stretchy, supports joints | Helps brain and protects cells |
How They Complement Each Other
Collagen and glycine work together to keep your body healthy. Glycine is needed to make collagen because it fits into every third spot in collagen’s triple-helix shape. Without enough glycine, your body can’t make strong collagen, which weakens tissues and slows repairs.
By eating or taking both collagen and glycine, you can get the best results. Collagen gives your body the support it needs, while glycine makes sure collagen is made properly. Together, they are a great team for fighting aging and staying healthy.
Anti-Aging Benefits of Collagen
Skin Health and Elasticity
Smoothing Wrinkles and Fine Lines
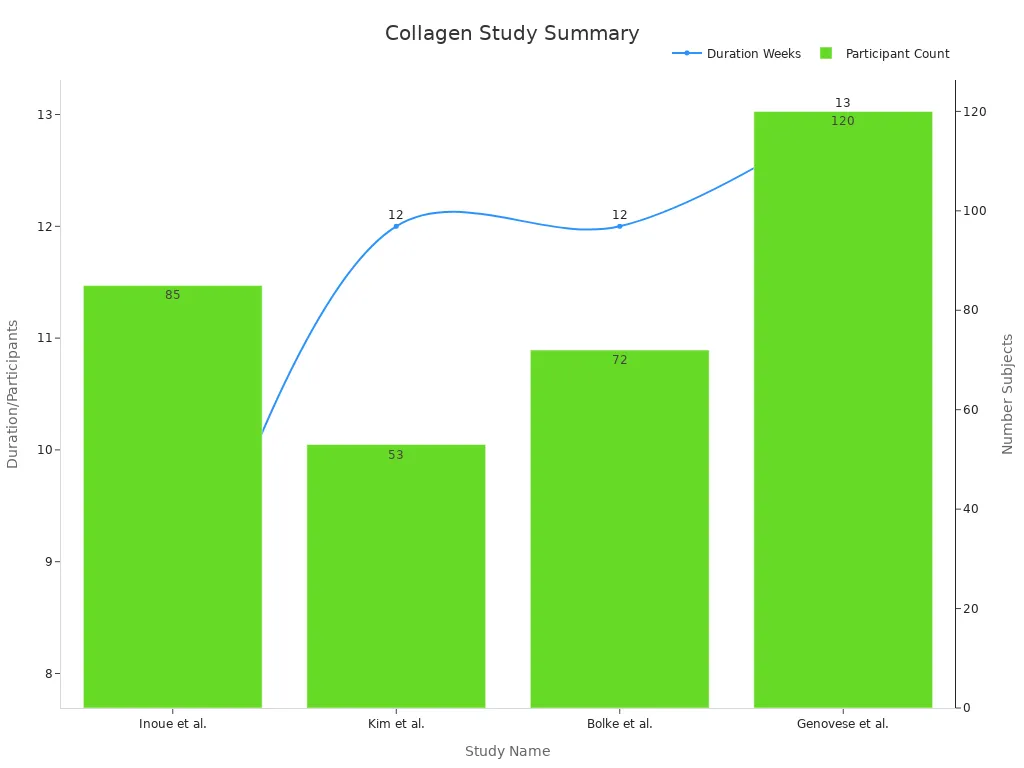
Collagen supplements can help reduce wrinkles and fine lines. As you grow older, your body makes less collagen. This causes your skin to become thinner and less stretchy. Taking collagen can help rebuild your skin’s structure. Studies support this. For example, research by Inoue et al. showed that 85 women had fewer wrinkles and better skin moisture after eight weeks of collagen use.
Here’s a summary of some study results:
Study | Participants | Duration | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
Inoue et al. | 85 women | 8 weeks | Better skin moisture and fewer wrinkles. |
Kim et al. | 53 women (ages 40-60) | 12 weeks | Improved skin hydration and fewer wrinkles. |
Bolke et al. | 72 women (ages >35) | 12 weeks | Better skin hydration, elasticity, and smoothness. |
Genovese et al. | 120 people | 90 days | Higher self-reported skin health, no big change in elasticity. |
Boosting Skin Hydration and Firmness
Collagen doesn’t just help with wrinkles; it also keeps your skin hydrated and firm. It helps your skin hold water, making it look fuller and healthier. A study by Bolke et al. found that women who took collagen for 12 weeks had much better skin hydration and elasticity. Imagine waking up with soft, firm, and refreshed skin every day!
Joint and Bone Support
Helping Joints Move and Reducing Pain
Collagen isn’t just for your looks—it helps you feel better too. If your joints feel stiff or sore, collagen might help. It supports the cartilage in your joints, which cushions them and reduces friction. Research shows that collagen peptides can ease joint pain and slow bone loss.
Here’s what studies found:
Evidence Type | Findings |
|---|---|
Meta-analysis | |
Chondrocyte Stimulation | Collagen supplements boost type II collagen production in joints. |
Bone Loss Prevention | Collagen helps keep bones strong by improving their organic content. |
By helping your joints move better and reducing pain, collagen can keep you active and enjoying life.
Hair and Nail Strength
Supporting Growth and Preventing Breakage
Do your nails break easily, or does your hair feel thin? Collagen can help with that too. It gives your body what it needs to make stronger hair and nails. One study found that collagen increased nail growth by 12% in 24 weeks and reduced nail breakage by 42%. Another study by Hexsel et al. showed that collagen made nails less brittle and healthier.
Study Reference | Findings | Implications |
|---|---|---|
Unspecified Study | Nail growth increased by 12% in 24 weeks, and nail breakage dropped by 42%. | Shows collagen’s benefits for nail strength. |
Hexsel et al., 2017 | Collagen improved nail growth and reduced brittleness. | Proves collagen helps nail health. |
For hair, collagen supports the structure of hair follicles. This makes hair stronger, shinier, and less likely to break. Adding collagen to your routine could be the key to healthier hair and nails!
Anti-Aging Benefits of Glycine
Supporting Collagen Production
How Glycine Enhances Collagen Synthesis
Glycine is very important for keeping skin smooth. It makes up about 33% of collagen’s structure. Without enough glycine, your body can’t make strong collagen. Glycine fits into collagen’s triple-helix shape every third spot. This placement helps collagen stay strong and stretchy. Strong collagen is needed for healthy skin and joints.
Studies show glycine does more than help collagen. It also speeds up skin repair. Glycine increases skin repair cells, helping wounds heal faster. When combined with royal jelly, glycine works even better. Together, they boost collagen production and skin healing.
Evidence Description | Findings |
|---|---|
Glycine’s role in collagen | Glycine makes up 33% of collagen, helping its production. |
Effects on skin repair | Glycine boosts skin repair cells for faster healing. |
Synergistic effects | Glycine and royal jelly together improve collagen synthesis. |
Adding glycine to your routine can help your body make more collagen.
Cellular Repair and Antioxidant Effects
Role in Glutathione Production
Glycine doesn’t just help collagen—it repairs your cells too. It helps make glutathione, a strong antioxidant. Glutathione protects cells from damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals can speed up aging. Glycine boosts glutathione levels, fighting oxidative stress and keeping cells healthy.
Glycine also helps fix damaged DNA. Studies show cancer cells without glycine are weaker against radiation. This proves glycine helps repair DNA and protect cells. Glycine gives your body extra defense against aging and stress.
Glycine helps make glutathione, which protects cells.
It repairs DNA, helping cells recover from damage.
Without glycine, cells are weaker against stress, showing its importance.
Sleep and Recovery
Improving Sleep Quality for Better Regeneration
Glycine can help you sleep better. Sleep is important for your body to repair itself. Glycine calms your brain and lowers body temperature. This helps you fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer.
Good sleep helps your body recover. While sleeping, your body fixes tissues, makes collagen, and fights aging. Taking glycine helps your body heal overnight. Imagine waking up refreshed with healthier skin and joints. That’s what glycine can do.
Tip: Trouble sleeping? Try glycine before bed. It’s a natural way to improve sleep and recovery.
Comparing Effectiveness for Anti-Aging
When to Choose Collagen
Best for Skin and Hair Improvements
If you want better skin and hair, choose collagen. It helps your skin stay firm, hydrated, and smooth. Collagen reduces wrinkles and fine lines, making your skin look younger. Studies show that taking collagen with vitamin C can improve skin in just 12 weeks.
For example, women aged 40-60 took 1,000 mg of collagen peptides and 100 mg of vitamin C. Their skin became more hydrated, and wrinkles reduced. The group that only took vitamin C saw no big changes. This shows how collagen can make a visible difference in your skin.
Collagen also helps your hair grow stronger. It supports hair follicles, which can reduce thinning and breakage. If your hair feels weak, collagen can bring back its shine and thickness. It works from the inside to improve both skin and hair.
Best for Joints and Bones
Collagen is great for keeping joints and bones healthy. It helps cartilage, which cushions your joints, and supports bone strength. As you age, your body makes less collagen, which can cause joint pain and weaker bones. Taking collagen can help prevent these problems.
Research shows collagen peptides help your body make type II collagen, which improves joint movement and reduces pain. Collagen also strengthens bones, making them less likely to break. If you want to stay active and pain-free, collagen is a smart choice.
When to Choose Glycine
Best for Cell Health
Glycine is important for keeping your cells healthy. It helps protect your cells from damage and supports DNA repair. Glycine also helps make glutathione, a powerful antioxidant. Glutathione fights free radicals, which can harm your cells and speed up aging.
Without enough glycine, your cells are weaker and more likely to get damaged. If you want to protect your body from the inside, glycine is a great option.
Best for Making Collagen Naturally
Instead of taking collagen directly, glycine helps your body make its own. Glycine makes up about one-third of collagen’s structure. Without enough glycine, your body can’t make strong collagen.
Glycine also helps repair skin by boosting skin repair cells. This makes it good for healing wounds and keeping skin healthy. If you prefer to help your body produce collagen naturally, glycine is the way to go.
Aspect | Collagen Benefits | |
|---|---|---|
Muscle Repair | Helps muscles heal and recover | Supports muscle growth and recovery |
Brain Function | Improves sleep, memory, and focus | N/A |
Energy and Metabolism | Balances blood sugar and boosts energy | N/A |
Antioxidant Effects | Protects cells from damage | N/A |
Gut Health | Supports digestion and immunity | Repairs the gut lining |
Aging | Slows aging with antioxidants | Improves skin, hair, and nails |
Hormone Balance | Helps balance hormones by supporting the liver | Boosts muscle metabolism |
Sources | Found in bone broth and supplements | Comes from animal parts like skin and bones |
Combining Collagen and Glycine
Why Use Both Together
Collagen and glycine work better as a team. Collagen gives your body the support it needs, while glycine helps your body make collagen. Together, they fight aging by improving skin, hair, and joints while protecting your cells.
For example, glycine makes collagen supplements work even better by boosting collagen production. At the same time, collagen provides the building blocks your body needs for strong tissues. Using both gives you the best results for anti-aging.
If you want full-body support, try using both collagen and glycine. They can help you feel and look your best, inside and out.
Practical Recommendations for Anti-Aging Supplements
Picking a Collagen Supplement
Types of Collagen (Type I, II, III)
Choosing the right collagen type depends on your goals. The three main types for aging are:
Type I: Found in skin and bones. It helps reduce wrinkles.
Type II: Supports joints by keeping cartilage healthy.
Type III: Works with type I to improve skin and muscles.
For more benefits, pick supplements with multiple collagen types. This helps both skin and joints. Check the source too. Marine collagen absorbs well, while bovine collagen has types I and III. If you have diet limits, read the label carefully.
Hydrolyzed Collagen vs. Gelatin
Collagen comes as hydrolyzed collagen (collagen peptides) or gelatin. Hydrolyzed collagen is broken into small pieces, so it’s easy to absorb. It mixes into drinks and helps skin and joints.
Gelatin is less processed and good for cooking. Use it in soups or gummies. Both forms help aging, but hydrolyzed collagen is easier for daily use.
Tip: Want quick results? Try hydrolyzed collagen. It’s easier to digest.
Picking a Glycine Supplement
Forms of Glycine (Powder, Capsules)
Glycine comes in two forms:
Powder: Mix it into tea or smoothies. It’s flexible and affordable.
Capsules: Easy to carry and pre-measured for convenience.
Choose high-quality glycine with clear labels to ensure safety.
Dosage Guidelines for Anti-Aging
For aging, take 2 to 5 grams of glycine daily. Start small and increase slowly. Glycine is safe, but ask your doctor before starting any new supplement.
Food vs. Supplements
Foods High in Collagen and Glycine
Boost collagen and glycine naturally by eating these foods:
Collagen foods: Bone broth, chicken skin, and fish skin.
Glycine foods: Meat, fish, and gelatin. Soybeans and seeds also have glycine.
Here’s a quick comparison:
Protein Source | Total Protein (g) | Glycine (mg) | Collagen Content |
|---|---|---|---|
Beef Broth | Moderate | High | |
Dairy Proteins | 19.3 ± 0.8 | Lower | None |
Collagen Proteins | 19.3 ± 0.8 | Higher | High |
When to Use Supplements
Foods are great but may not give enough collagen or glycine. Supplements provide higher doses and are easy to use. They help with skin, joints, and cell repair.
Note: Supplements are useful if you’re busy or can’t eat enough collagen-rich foods.
Collagen and glycine each offer special anti-aging benefits. Collagen helps improve your skin, hair, and joints. Glycine works inside your body, helping make collagen and protecting cells.
Tip: Use both for better results. Collagen gives support, and glycine helps your body use it well.
Pick based on your goals, but talk to a doctor first. Choosing the right supplement now can help you stay healthy as you age!
FAQ
1. Can you take collagen and glycine together?
Yes, you can take both at the same time! Collagen helps support your body’s structure, while glycine helps make more collagen and fixes cells. Using them together boosts anti-aging benefits for your skin, joints, and health.
Tip: Use both for the best results!
2. How long does it take to see results from collagen supplements?
Most people see better skin hydration and firmness in 8-12 weeks. For joint or hair improvements, it might take longer. Stay consistent with your routine to get the best results.
3. Is glycine better than collagen for anti-aging?
It depends on what you need. Glycine helps your body make collagen and repairs cells. Collagen directly improves your skin, hair, and joints. For the best anti-aging effects, use both together.
4. Are there any side effects of taking collagen or glycine?
Both are usually safe to use. Some people may feel mild stomach upset with collagen. Glycine is safe but might make you sleepy if you take too much. Follow the recommended dose and ask your doctor if unsure.
5. Can vegetarians or vegans take collagen or glycine?
Collagen comes from animals, so it’s not vegetarian or vegan. Glycine can come from plants like soybeans and seeds. Vegans can focus on plant-based glycine foods or supplements.
6. What’s the best time to take collagen or glycine?
You can take collagen anytime, but many prefer it in the morning or with meals. Glycine works well before bedtime because it helps you sleep better. Pick a time that fits your schedule.
7. Do collagen and glycine help with weight loss?
Collagen helps keep muscles strong and may reduce hunger, which can help with weight control. Glycine balances blood sugar and boosts energy use. While they don’t directly cause weight loss, they support a healthy lifestyle.
Note: Combine supplements with good food and exercise for better results.
8. Can I get enough collagen and glycine from food alone?
You can get some from foods like bone broth, chicken skin, and fish. But it’s hard to eat enough for big anti-aging effects. Supplements are an easier way to get more collagen and glycine.
Tip: Use supplements if your diet doesn’t include enough collagen or glycine foods.



1 comment