Keeping blood sugar levels steady is very important for people with Type 2 diabetes. Berberine supplements might help with this. Studies show they can improve health in many ways.
A review of 18 studies showed berberine lowers fasting blood sugar. It also reduces insulin resistance and improves cholesterol.
Another review of 14 studies found berberine works as well as drugs like metformin and glipizide to lower blood sugar.
Taking 600–2,700 mg daily can cut fasting blood sugar by 20%. It can also lower long-term blood sugar levels by 12%.
These studies show berberine may help manage diabetes better.
Key Takeaways
Berberine pills can lower blood sugar by about 20%.
Studies say berberine works as well as drugs like metformin.
Take 1,000 to 1,500 mg daily before meals for best results.
Berberine helps your body use sugar better by improving insulin.
It helps your stomach by growing good bacteria and lowering swelling.
Eating healthy and exercising make berberine work even better.
Talk to your doctor before using berberine, especially with other medicines.
Upset stomach and feeling sick are common but go away fast.
How berberine works for diabetes
Improving insulin sensitivity
Berberine helps your body respond better to insulin. It turns on a protein called AMPK, which controls energy in cells. This action helps move glucose into cells by using a protein called GLUT4. Berberine also adds more insulin receptors to cells, making them work better with insulin.
Dr. Bradley says, “Berberine does two things: It helps insulin move glucose into cells and helps cells use glucose better.” Research shows berberine lowers fasting blood sugar and HbA1c, which are important for diabetes care. It also stops the liver from making too much glucose by blocking gluconeogenesis.
Regulating glucose metabolism
Berberine helps control how your body uses glucose. It activates AMPK, which breaks down glucose and fats for energy. This lowers blood sugar and balances energy. Berberine also blocks α-glucosidase, an enzyme that turns carbs into glucose in the gut. By slowing this, less glucose enters your blood after eating.
Studies show berberine lowers fasting blood sugar, post-meal sugar, and HbA1c. A review found berberine improved these markers more than control groups. It also reduces stress and swelling, which are common in diabetes.
Effects on gut microbiota
Your gut health affects diabetes, and berberine helps your gut bacteria. It grows good bacteria and reduces harmful ones. This balance helps digestion and lowers swelling, improving health.
Research says berberine’s gut effects may help control blood sugar. By lowering swelling, it improves insulin use and glucose control. This makes it useful for managing Type 2 diabetes.
Effectiveness of berberine supplements
Clinical studies on blood sugar control
Berberine has been studied a lot for lowering blood sugar. Research shows it helps manage Type 2 diabetes. One review of 18 studies found berberine lowers fasting blood sugar (FBS). It also improves cholesterol by lowering triglycerides (TG) and bad cholesterol (LDL). At the same time, it raises good cholesterol (HDL). These changes help people with diabetes stay healthier.
Another study compared berberine to diabetes drugs like metformin and glipizide. It showed berberine works just as well to lower blood sugar. A trial on prediabetes showed it reduces fasting glucose (FPG), post-meal glucose (2hPG), and HbA1c. This means it can improve insulin resistance and blood sugar control.
Study Type | Outcome | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
Lowered blood sugar levels | As effective as metformin, rosiglitazone, and glipizide | |
Meta-analysis of 18 trials | Reduced TG, FBS, LDL; increased HDL | Improved type II diabetes and reduced insulin resistance |
Clinical trial on prediabetes | Significant reduction in FPG, 2hPG, HbA1c | Improved insulin resistance and blood glucose levels |
Impact on fasting glucose and HbA1c
Berberine helps lower fasting glucose and HbA1c levels. These are important for checking diabetes. A study using HIMABERB® Berberine showed big drops in FPG and HbA1c after 84 days. This proves berberine can lower blood sugar in prediabetic people.
Parameter | Result |
|---|---|
FPG | |
HbA1c | Significant reduction observed |
Another study gave more details about these reductions. It showed clear drops in FPG, 2hPG, and HbA1c. The results were strong, with p-values under 0.01. This confirms berberine helps control blood sugar.
Parameter | Mean Difference (MD) | 95% CI | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
FPG | -0.39 | (-0.63, -0.16) | 0.001 |
2hPG | -1.51 | (-2.43, -0.59) | 0.001 |
HbA1c | -0.20 | (-0.32, -0.08) | 0.002 |
Long-term benefits and limitations
Berberine has long-term benefits for diabetes care. It lowers FPG, 2hPG, and HbA1c while helping with insulin resistance. For prediabetes, it may stop or slow the move to Type 2 diabetes. It also helps the heart by lowering cholesterol and triglycerides. Berberine is affordable and works well with healthy habits.
But there are some limits. Berberine cannot replace healthy lifestyle changes. These are still needed to manage diabetes and protect the heart. People on metformin should ask their doctor before using berberine. It might make metformin less effective by 25%. Older people or long-term users may see less benefit. Bigger studies are needed to check its safety over time.
Berberine may stop prediabetes from becoming Type 2 diabetes.
It improves cholesterol and triglycerides, helping heart health.
It is safe, affordable, and works with healthy habits.
Limits include less effect in older people and drug interactions.
Safety and side effects of berberine
Common side effects
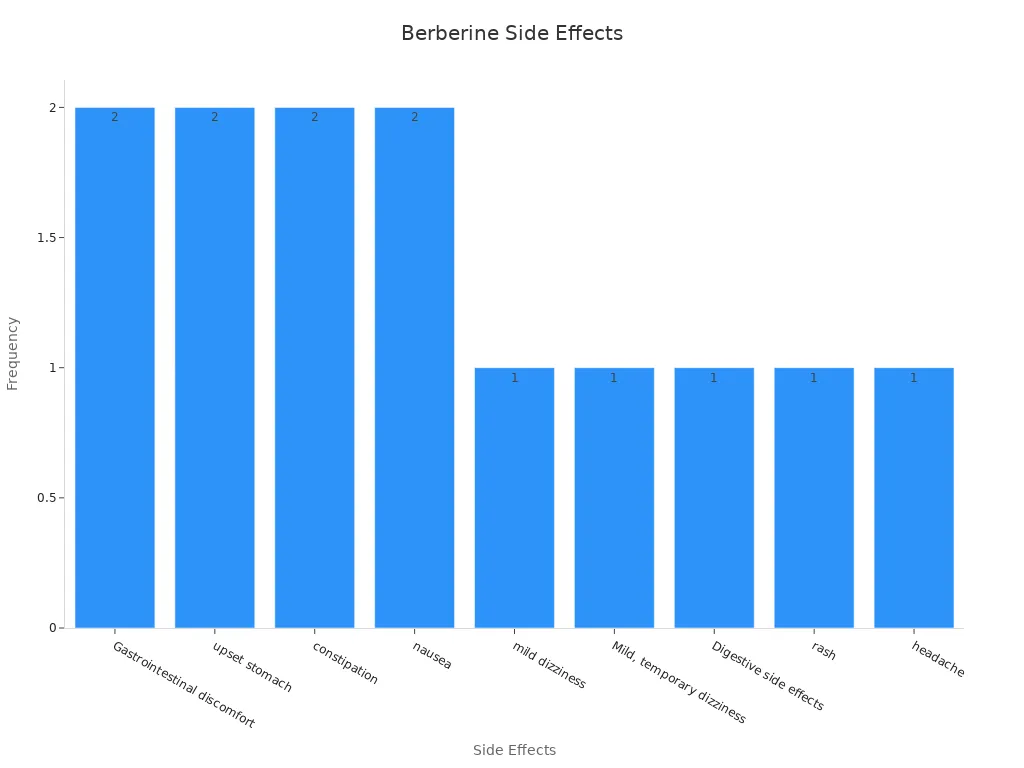
Berberine is safe for most people but may cause mild issues. These problems are usually not serious and go away quickly. Common side effects include stomach upset, nausea, or constipation. Some people might feel a little dizzy or get headaches.
Source | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|
Integrative Pro | Stomach upset, nausea, constipation, mild dizziness |
Clinical Observational Study | Temporary dizziness, stomach discomfort |
WebMD | Digestive issues, nausea, constipation, rash, headache |
Studies show serious side effects are rare. Most people handle berberine well, making it a good option for diabetes care. If symptoms are severe or last long, talk to your doctor.
Who should avoid berberine
Some people should not take berberine. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid it because it may harm the baby. It could make jaundice worse in newborns. Kids under 18 should also skip berberine due to possible risks seen in animal studies.
People allergic to berberine or with certain health problems should avoid it too. Always ask your doctor before starting berberine, especially if you have health concerns.
Medication interactions and risks
Berberine can mix poorly with some medicines, so be careful. It might interfere with diabetes drugs like metformin, making them less effective. Berberine also changes how the liver handles medicines, which could affect their results.
Other risks include:
Dropping blood sugar too low when combined with diabetes medicine.
Lowering blood pressure too much if taken with blood pressure drugs.
Causing extra sleepiness when used with sedatives.
Berberine may block liver enzymes like cytochrome P450 2D6, 2C9, and 3A4. This can change how some medicines work. To stay safe, always check with your doctor before using berberine, especially if you take prescription drugs.
Dosage recommendations for berberine
Typical dosage for Type 2 diabetes
Berberine doses for Type 2 diabetes depend on personal needs. Most studies suggest taking 1,000 to 1,500 mg daily. Split this into smaller doses before meals, like 500 mg three times a day. This helps with insulin and blood sugar control. Higher doses, between 600 and 2,700 mg daily, have also been tested. These higher amounts showed good results in lowering blood sugar.
Dosage Range (mg) | Description |
|---|---|
600 – 2,700 | Doses tested in clinical studies |
1,000 – 1,500 | Commonly recommended daily amount |
2 – 3 capsules | Equals 1,000 – 1,500 mg daily |
Pick a dose based on your health goals. Lower doses may help with blood sugar, while higher ones might aid weight loss. Start with the suggested dose and adjust under a doctor’s advice.
Best practices for taking berberine
To get the best results, follow these tips. Take berberine before meals to help your body absorb it better. Splitting your daily dose into smaller amounts can prevent side effects like stomach upset. For example, if you take 1,500 mg daily, divide it into three doses of 500 mg each.
Be consistent. Take berberine at the same time every day to keep steady levels in your body. Pair it with healthy eating and exercise for better results. Studies show berberine works well with lifestyle changes, improving cholesterol and blood sugar.
Study Type | Number of Trials | Dosage Range (mg) | Duration (weeks) | Total Cholesterol Reduction (mmol/L) | LDL Cholesterol Reduction (mmol/L) | Triglycerides Reduction (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Meta-analysis | 16 | 600–1,500 | 1–24 | 0.47 | 0.38 | 0.28 |
Systematic Review | 11 | 500–1,500 | 8–52 | 0.61 | 0.65 | 0.50 |
If you feel mild side effects, try taking berberine with food. You can also lower the dose for a short time to let your body adjust.
When to consult a healthcare provider
Talk to your doctor before starting berberine to make sure it’s safe. Some conditions or medicines may need extra care. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid berberine. It could harm the baby or worsen jaundice in newborns. Kids under 18 should not take berberine because there isn’t enough research on its safety for them.
Contraindication | Description |
|---|---|
Pregnancy | May harm the unborn baby. |
Breastfeeding | Could worsen jaundice in infants. |
Age under 18 | Not safe for children or teens. |
Certain medications | Check with a doctor if taking other drugs. |
Berberine might interact with medicines like metformin or blood pressure pills. This could change how they work. If you take prescription drugs, talk to your doctor first. This will help you safely add berberine to your diabetes care plan.
Comparing berberine to other diabetes treatments

Berberine vs. standard diabetes medications
Berberine works as well as common diabetes drugs like metformin. Studies show it lowers fasting blood sugar (FPG), two-hour post-meal sugar (2hPG), and HbA1c levels. A review of 14 studies confirms berberine is as effective as metformin, rosiglitazone, and glipizide for managing blood sugar.
Measurement | Berberine Effect | Metformin Effect | Statistical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
FPG | N/A | P = 0.001 | |
2hPG | MD = −1.51 | N/A | P = 0.001 |
HbA1c | MD = −0.20 | N/A | P = 0.002 |
Berberine also helps improve cholesterol. It lowers triglycerides and bad cholesterol (LDL) while raising good cholesterol (HDL). However, you should not stop taking prescribed medicines without asking your doctor first.
Berberine vs. lifestyle changes
Healthy eating and exercise are key to managing diabetes. Berberine works well with these habits by improving insulin use and lowering blood sugar. Studies show combining berberine with a healthy lifestyle gives better results. For example, it can lower fasting glucose and HbA1c while helping with weight loss.
Berberine helps lower blood sugar and improves insulin use.
It works best when paired with healthy eating and exercise.
Do not replace medicines or healthy habits with berberine alone.
If you already follow a healthy lifestyle, adding berberine may help more. But using only berberine without making healthy changes may not work as well.
Combining berberine with other treatments
Berberine can boost the effects of other diabetes treatments. Studies show it works well with blood-sugar-lowering drugs like metformin. For example, research in the DMS Journal found berberine helps control FPG, 2hPG, and HbA1c in people with prediabetes.
Study | Findings |
|---|---|
Medical News Today | Berberine combined with diabetes drugs works better than drugs alone. |
Berberine makes diabetes medicines like metformin work better.
Combining berberine with other treatments can improve blood sugar control.
If you want to add berberine to your treatment plan, talk to your doctor. They can help you find the right dose and check for any risks with your current medicines.
Key considerations before using berberine
Importance of medical advice
Talk to your doctor before starting berberine. This ensures it is safe for you. Some people should not take berberine, especially if they use other medicines. It can mix poorly with drugs processed by the liver, like cytochrome P450. These mixes might make your medicines work less or cause side effects.
If you have diabetes, your doctor can help you add berberine safely. They will check if it works well and doesn’t harm you.
Tip: Always tell your doctor about all medicines or supplements you take. This helps avoid bad interactions and keeps you safe.
Factors to consider (e.g., age, health conditions)
Your health affects how well berberine works. If you have heart, liver, or kidney problems, it may not work as well. These issues can also raise the chance of side effects. For example, liver problems may change how your body handles berberine, causing unexpected results.
Using berberine with healthy habits, like eating well and exercising, works better. Studies show this combo improves blood sugar and cholesterol more than berberine alone.
Factor | Impact on Berberine Effectiveness |
|---|---|
Heart disease | May reduce effectiveness |
Liver or kidney problems | Alters how berberine is processed |
Lifestyle changes | Boosts effectiveness |
Age doesn’t seem to affect how berberine works. But older people should still ask their doctor to make sure it’s safe.
Monitoring blood sugar while using berberine
Checking your blood sugar is important when taking berberine. Studies show it lowers fasting glucose (FPG), post-meal glucose (2hPG), and HbA1c levels. These effects are stronger when paired with healthy habits.
To track your progress:
Use a glucometer to check blood sugar often.
Write down fasting and after-meal sugar levels.
Share these numbers with your doctor during visits.
A study of 859 prediabetic people found berberine works like metformin to lower blood sugar. This shows it can help manage diabetes. But proper tracking is key to staying safe and getting good results.
Note: If your blood sugar drops too low, call your doctor right away. You may need to change your dose or plan.
Berberine supplements may help control blood sugar in type 2 diabetes. Research shows they lower fasting glucose and HbA1c levels well, similar to medicines like metformin.
Study Details | Results |
|---|---|
Review of 14 studies | Berberine reduced blood sugar as effectively as metformin, rosiglitazone, and glipizide. |
HIMABERB® Study | FPG and HbA1c dropped below prediabetes levels after 84 days of treatment. |
Follow the right dosage to use berberine safely.
Take 1,000–1,500 mg daily, split into three doses before meals.
It can reduce fasting blood sugar by 20% and HbA1c by 12%.
Talk to your doctor before starting berberine. With healthy habits, it can improve your diabetes care plan.
FAQ
What is berberine, and where does it come from?
Berberine is a natural substance from plants like barberry and goldenseal. It has been used for centuries in traditional medicine to treat infections and stomach problems.
How does berberine help with Type 2 diabetes?
Berberine activates AMPK, a protein that controls energy in cells. This lowers blood sugar, improves insulin use, and reduces sugar made by the liver. It also slows how carbs turn into sugar in the gut.
Can I take berberine with my diabetes medication?
You can take berberine with diabetes medicine, but ask your doctor first. It might change how drugs like metformin work or increase the chance of low blood sugar.
How long does it take for berberine to show results?
Most people see lower blood sugar in 8 to 12 weeks. Results depend on your dose, health, and habits like diet and exercise.
Are there any side effects of taking berberine?
Berberine is usually safe but may cause mild issues like nausea or constipation. These often go away as your body gets used to it. If problems continue, talk to your doctor.
Who should avoid taking berberine?
Pregnant women, breastfeeding moms, and kids under 18 should not take berberine. People with certain health problems should also avoid it. Always check with your doctor first.
Can berberine replace my diabetes medication?
Berberine cannot replace your diabetes medicine. It works best with healthy habits and your current treatments. Follow your doctor’s advice for managing diabetes.
What is the best way to take berberine?
Take berberine before meals to help your body absorb it. Split your daily dose, like 500 mg three times a day, to avoid side effects and keep steady levels.
Does berberine help with weight loss?
Berberine may help with weight loss by improving how your body uses energy. Studies show it can reduce body weight and belly fat, especially with a healthy diet and exercise.