Recent studies show that both type I and type III hydrolyzed collagen peptides help improve skin by boosting moisture, elasticity, and reducing wrinkles. Type I collagen makes up most of your skin’s collagen and supports overall skin health, while type III collagen aids in repair and structure. You should consider your unique skin goals before choosing a supplement.
This article provides information for educational purposes only. Please consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Key Takeaways
Type I collagen is the main protein that gives your skin strength, firmness, and helps reduce wrinkles.
Type III collagen supports skin repair, elasticity, and helps your skin heal after damage.
Hydrolyzed collagen peptides are broken-down collagen pieces that your body absorbs easily to boost skin health.
Supplements with both type I and type III collagen provide balanced benefits for skin strength and repair.
Marine collagen absorbs quickly and mainly contains type I, while bovine collagen offers both types I and III.
Taking 2.5 to 10 grams of hydrolyzed collagen daily for 8 to 12 weeks can improve skin hydration, elasticity, and smoothness.
Choose collagen supplements with added vitamin C and other nutrients to support your body’s natural collagen production.
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting collagen supplements, especially if you have allergies or health conditions.
Collagen and Skin
What Is Collagen?
You encounter collagen every day, even if you do not realize it. Collagen is the most abundant protein in your body. It forms a strong network of fibers that gives structure and support to your skin, bones, muscles, and tendons. In your skin, collagen acts as a scaffold, holding everything together and helping your skin stay firm and smooth.
There are several types of collagen, but type I and type III are the most important for skin health. Type I collagen makes up about 90% of the collagen in your skin. Type III collagen works alongside type I, especially during growth and repair. Both types of collagen help your skin look youthful and resilient.
Did you know? Collagen is produced by cells called fibroblasts. These cells work hard to keep your skin strong and flexible.
Collagen’s Role in Skin
Collagen plays many roles in your skin. You need collagen for strength, elasticity, and hydration. Here are some key functions:
Collagen maintains the structure, stability, and strength of your skin’s dermal layers.
It interacts with elastin to help your skin stretch and bounce back.
Collagen helps your skin retain moisture, preventing dryness and dullness.
It supports wound healing and repair, especially after injury or damage.
Collagen provides essential building blocks for other proteins, like elastin and hyaluronic acid.
As you age, your body produces less collagen. Sun exposure, pollution, and other environmental factors also slow down collagen production. When collagen levels drop, your skin becomes thinner, less elastic, and more prone to wrinkles. You may notice sagging, dryness, and slower healing.
Clinical studies show that oral collagen peptide supplements can help your skin. These supplements provide amino acids and bioactive peptides that stimulate your fibroblasts. As a result, your skin may become more hydrated, elastic, and firm. Many people see fewer wrinkles and improved skin texture after regular collagen intake.
Collagen Function | Skin Benefit |
|---|---|
Structure & Stability | Firmness, resilience |
Elasticity | Stretch, bounce-back |
Hydration | Moisture, smoothness |
Repair | Wound healing, regeneration |
You can support your skin by choosing the right types of collagen supplements. Type I collagen is best for overall skin strength and appearance. Type III collagen helps with repair and structure, especially if your skin needs extra support.
Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides
What Are Hydrolyzed Collagen Peptides?
You may wonder what makes hydrolyzed collagen peptides different from regular collagen. Hydrolyzed collagen peptides are small protein fragments created by breaking down larger collagen molecules. Manufacturers use several methods to produce these peptides. They often rely on enzymatic hydrolysis, which uses enzymes to cut collagen into smaller, bioactive pieces. Some processes use microbial fermentation or chemical hydrolysis, depending on the desired properties.
These peptides come from collagen-rich sources such as bovine, porcine, or marine materials like skin, scales, and bones. During production, the triple-helix structure of native collagen unravels, and the enzymes break it into shorter chains. The result is a mixture of peptides with low molecular weight, usually between 3 and 6 kilodaltons. This smaller size makes hydrolyzed collagen peptides easier for your body to handle.
Hydrolyzed collagen has unique properties. It dissolves well in water, has low viscosity, and mixes easily into drinks or foods. The degree of hydrolysis, or how much the collagen is broken down, affects the length of the peptides and their benefits. These peptides support your skin, cartilage, and other tissues by providing building blocks and signaling molecules.
Absorption and Effectiveness
Your body absorbs hydrolyzed collagen peptides much more efficiently than intact collagen or gelatin. After you consume hydrolyzed collagen, your digestive system breaks it down further into dipeptides and tripeptides. Special transporters in your gut, such as PepT1, help move these small peptides into your bloodstream. Studies show that over 90% of hydrolyzed collagen peptides are absorbed, which is much higher than other protein sources.
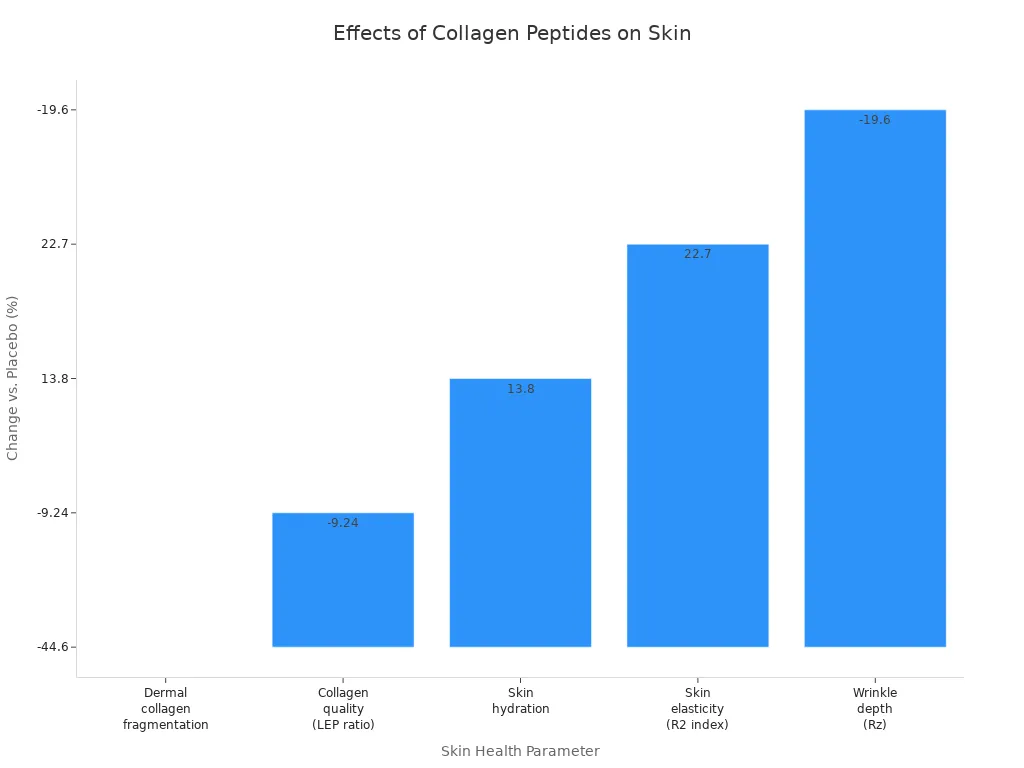
Once in your blood, these peptides travel to your skin and other tissues. They stimulate your fibroblasts, the cells responsible for making new collagen. You can see the effects in your skin’s hydration, elasticity, and appearance. Clinical research supports these collagen benefits. For example, after 12 weeks of taking hydrolyzed collagen peptides with vitamin C, people experienced:
Skin Parameter | Result vs. Placebo | Significance |
|---|---|---|
Dermal collagen fragmentation | 44.6% decrease | p < 0.01 |
Skin hydration | 13.8% increase | p < 0.01 |
Skin elasticity | 22.7% increase | p < 0.01 |
Wrinkle depth | 19.6% decrease | p < 0.01 |
Hydrolyzed collagen peptides deliver amino acids like glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline directly to your skin. These nutrients help your skin cells build new collagen fibers and repair damage. You may notice smoother, firmer, and more hydrated skin after regular use. Collagen benefits also include improved wound healing and support for your joints and bones.
Note: This information is for educational purposes only. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Type I Collagen
Type I Collagen in Skin
You find type I collagen as the main building block in your skin. This type makes up about 85–90% of the total collagen in adult skin, giving your skin its strength and structure. Type I collagen spreads evenly throughout the dermal and subdermal layers. You see finer collagen fibrils in the papillary region just beneath the epidermis, while the reticular region deeper in the dermis contains larger, denser bundles. As you grow, the diameter of these fibrils increases, which helps your skin resist stretching and tearing.
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Collagen Type I Proportion | 70–75% of total collagen in fetal skin; increases to 85–90% in adult skin |
Distribution | Evenly distributed throughout dermal and subdermal connective tissue; intensified at dermal-epidermal junction |
Dermis Regions | Papillary region: finer collagen fibrils, more cells, beneath epidermis |
Reticular region: larger fibrils, denser collagen, deeper dermis | |
Collagen Fibril Development | Fibril diameter and fiber bundle size increase with gestational age |
Functional Role | Provides structural integrity and mechanical strength; contributes to tensile strength and dermal architecture support |
Collagen Fiber Orientation | Multidirectional; organization varies with mechanical forces exerted on skin |
Type I collagen fibers run in many directions. This arrangement lets your skin handle pressure and movement from different angles. You rely on this type for the mechanical strength and visual appearance of your skin.
Benefits of Type I Collagen
Elasticity
Type I collagen supports skin elasticity by forming a strong network of fibers. You notice that your skin stretches and returns to its original shape because of this type. When you supplement with type I collagen, you help your skin maintain elasticity and bounce. Clinical trials show that skin elasticity increases by 5.1% after regular intake of type I collagen supplements.
Hydration
You need hydration for smooth, healthy skin. Type I collagen helps your skin hold water, keeping it plump and soft. When you use type I collagen supplements, you boost your skin’s hydration by 4.3%. This improvement makes your skin look brighter and feel more comfortable.
Wrinkle Reduction
Wrinkles form when your skin loses collagen and elasticity. Type I collagen helps reduce wrinkles by supporting the structure and firmness of your skin. Studies show that type I collagen supplementation can decrease wrinkles by 27.5%. You see fewer lines and a smoother texture when you keep your collagen levels high.
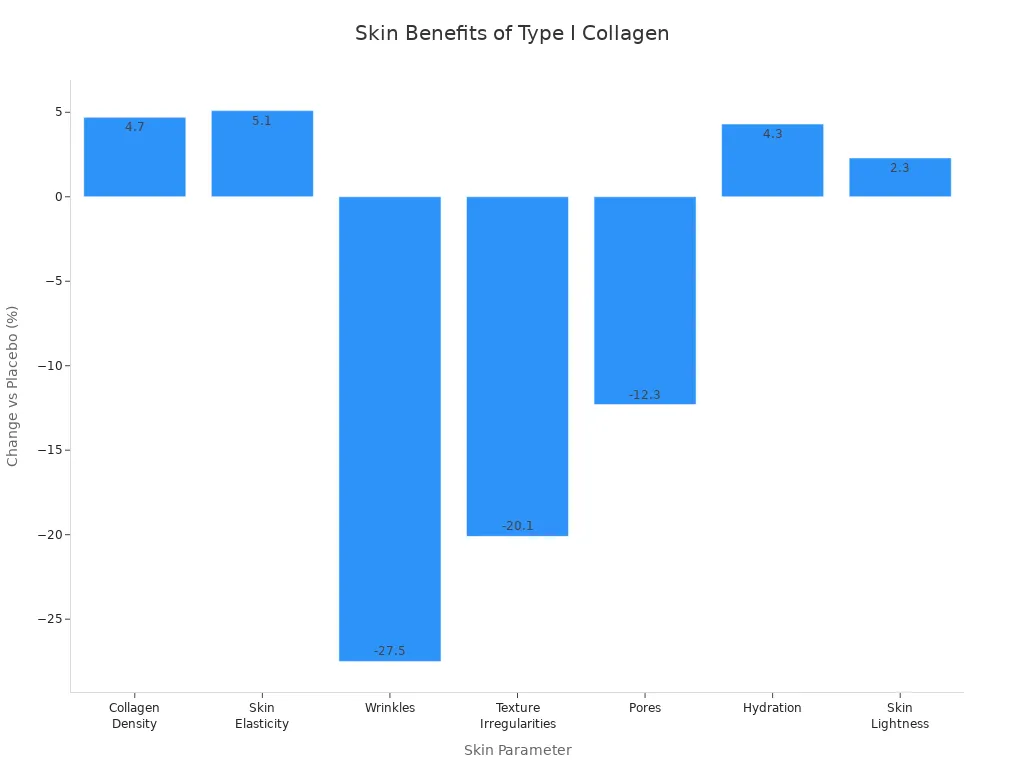
Skin Parameter | Effect of Vegan Collagen Supplementation vs Placebo |
|---|---|
Collagen Density | Increased by 4.7% |
Skin Elasticity | Increased by 5.1% |
Wrinkles | Decreased by 27.5% |
Texture Irregularities | Decreased by 20.1% |
Pores | Decreased by 12.3% |
Hydration | Increased by 4.3% |
Skin Lightness | Increased by 2.3% |
You benefit from type I collagen in many ways. You see improvements in skin elasticity, hydration, and a reduction in wrinkles. These collagen benefits help you maintain a youthful visual appearance.
Sources of Type I Collagen
You can get type I collagen from several dietary and supplemental sources. Collagen supplements often use peptides from bones, tendons, skin, and fish scales. You find type I collagen in:
Bones, ligaments, tendons, and skin of animals
Bovine (cow) and fish-derived collagen peptides
Bone broth made by simmering animal bones
Unflavored gelatin from boiling animal bones, cartilage, and skin
Tough cuts of meat rich in connective tissue, such as pot roast or brisket
Skin and bones of fresh and saltwater fish
You also support collagen formation by eating foods rich in amino acids like glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline. These include fish, poultry, meat, eggs, dairy, legumes, and soy. Nutrients such as vitamin C, zinc, copper, and manganese help your body produce collagen. You find these in citrus fruits, berries, leafy greens, shellfish, nuts, seeds, and whole grains.
Tip: Choose hydrolyzed collagen peptides for better absorption and effectiveness. You help your skin by combining collagen-rich foods with nutrients that support collagen synthesis.
Medical Disclaimer: This information is for informational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice. You should consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Type III Collagen
Type III Collagen in Skin
You find type III collagen as the second most abundant type in your body. In your skin, type III collagen makes up about 8–11% of the dermal extracellular matrix. This type forms fibrils with smaller diameters than type I collagen. Type III collagen often co-assembles with type I collagen, creating hybrid fibrils. These hybrid structures help regulate the size and organization of collagen fibers. You rely on type III collagen to maintain the mechanical properties and structure of your skin. It supports the dermal matrix and helps your skin stay resilient.
Type III collagen plays a key role during growth and repair. You see its importance in fetal development and postnatal tissue maintenance. This type influences how your skin heals after injury. It controls the architecture of the extracellular matrix, which is the network that gives your skin strength and flexibility.
Benefits of Type III Collagen
Repair
You benefit from type III collagen when your skin needs repair. This type helps organize collagen fibers during tissue healing. It regulates fibril diameter and assembly, which is important for proper matrix formation. You see type III collagen working alongside type I collagen to restore your skin’s structure after damage. It helps balance regeneration and scarring, making your skin heal more efficiently.
Wound Healing
Type III collagen supports wound healing by guiding the formation of new tissue. You rely on this type to suppress excessive scar formation. It controls the activation of myofibroblasts, which are cells responsible for fibrosis and scarring. When your skin heals, type III collagen helps remodel the matrix and promotes scar-free healing. Experimental models show that increased type III collagen leads to better healing outcomes, such as in midgestational fetuses and certain animals like the African Spiny Mouse.
Supportive Role
You experience the supportive role of type III collagen in everyday skin health. This type works with type I collagen to maintain normal skin architecture. It modulates fibroblast activity and influences how cells respond to their environment. Type III collagen helps keep your skin firm and organized. It limits pathological scarring and supports the balance between regeneration and fibrosis.
Clinical studies show that supplements containing type III collagen improve skin moisture, elasticity, and wrinkle reduction. You may notice firmer, more radiant skin after regular use. Trials with collagen peptides rich in type III collagen report significant improvements in hydration, wrinkle number, and skin roughness. You can see benefits as early as six weeks, with effects lasting beyond the supplementation period.
Type III Collagen Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Repair | Organizes collagen fibers during healing |
Wound Healing | Suppresses excessive scarring, remodels matrix |
Supportive Role | Maintains skin architecture, modulates cell activity |
Tip: You can support your skin’s repair and healing by choosing supplements that contain both type I and type III collagen.
Sources of Type III Collagen
You find type III collagen in several animal-based sources. Most hydrolyzed collagen and gelatin supplements come from porcine or bovine origins. These sources provide both type I and type III collagen together. Marine collagen, which comes from fish and invertebrates, mainly contains type I collagen. You do not find type III collagen in plant-based foods, but some ingredients may help boost your body’s natural collagen production.
Porcine skin and bones
Bovine hides and connective tissue
Hydrolyzed collagen supplements (often a mix of type I and type III collagen)
Gelatin from animal sources
Supplements usually combine type I and type III collagen for maximum skin benefits. You should look for products that specify their collagen types and sources. Marine collagen is preferred for its bioavailability, but it does not provide type III collagen. If you want type III collagen, choose bovine or porcine-based supplements.
Medical Disclaimer: This information is for informational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice. You should consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Type I vs Type III Collagen

Structural Differences
You see type I and type III collagen as the main collagen types in your skin. Both have similar molecular weights, close to 280,000 Daltons, and they behave alike in solution. You notice that both types of collagen pack together in a liquid-like arrangement, forming strong triple-helical structures. Type I collagen contains two alpha 1 chains and one alpha 2 chain, while type iii collagen is made of three identical alpha 1 chains encoded by the COL3A1 gene.
Type I collagen forms thick fibrils that give your skin strength and structure. Type iii collagen creates thinner fibrils and often mixes with type I collagen in hybrid bundles. When these two types of collagen combine, type iii collagen helps regulate the diameter of the fibrils. This interaction keeps your skin flexible and resilient. You find type iii collagen in hollow organs, such as blood vessels and the uterus, but it also plays a key role in your skin’s repair processes.
Mutations in the COL3A1 gene can change the stability and diameter of type iii collagen fibrils. These changes may lead to clinical conditions like vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. The coexistence of type I and type iii collagen in your skin creates a network that supports both strength and flexibility.
Collagen Type | Molecular Structure | Fibril Diameter | Main Role in Skin |
|---|---|---|---|
Type I | 2 alpha 1 + 1 alpha 2 chains | Thick | Strength, structure |
Type III | 3 alpha 1 chains (COL3A1 gene) | Thin | Repair, flexibility |
Hybrid (I + III) | Mixed triple helices | Regulated by III | Balance of strength & repair |
You benefit from the unique structural properties of each collagen type. The combination of type I and type iii collagen creates a balanced skin matrix.
Skin Benefits Compared
You want to know how the skin benefits of type I and type iii collagen compare. Clinical studies show that both types of collagen improve skin elasticity, hydration, and firmness. You see type I collagen as the most abundant collagen type in your skin, supporting overall strength and reducing wrinkles. Type iii collagen works alongside type I, helping with repair and regeneration.
Recombinant humanized type iii collagen injections improve skin elasticity, firmness, and dermal thickness. You notice fewer wrinkles and brighter skin with fewer treatments.
Type I collagen injections increase skin thickness and reduce redness, especially in severe skin conditions.
Both collagen types contribute to skin rejuvenation, but they act through different biological mechanisms.
Vitamin C derivatives stimulate collagen production, with a stronger effect on type iii collagen gene expression. You may see better repair and maintenance when you support type iii collagen synthesis.
The ratio of type I to type iii collagen changes as you age. Type iii collagen decreases more in elderly skin, which may affect your skin’s ability to repair and regenerate.
Benefit | Type I Collagen | Type III Collagen |
|---|---|---|
Elasticity | Strong improvement | Strong improvement |
Firmness | Major contributor | Supports repair |
Wrinkle Reduction | Significant effect | Noticeable effect |
Hydration | Maintains moisture | Supports regeneration |
Repair/Wound Healing | Supports structure | Key role in healing |
Safety Profile | Well tolerated | Favorable, few reactions |
You gain the most skin strength and wrinkle reduction from type I collagen. You rely on type iii collagen for repair, healing, and maintaining a balanced skin matrix.
Which Is Better for Skin?
You may wonder which collagen type is best for your skin. Experts agree that type I collagen is the primary collagen type for skin health. You see the greatest improvements in firmness, elasticity, and wrinkle reduction when you use type I collagen supplements. Type iii collagen plays a supportive role, helping your skin repair and regenerate after damage.
You benefit most when you combine both collagen types. Supplements that contain both type I and type iii collagen provide a balanced approach to skin health. You support your skin’s structure with type I collagen and enhance repair with type iii collagen. The combination helps you maintain youthful, resilient skin.
No direct head-to-head clinical trials compare the effects of type I and type iii collagen for skin. However, studies show that both types of collagen contribute to skin rejuvenation. You may see different benefits depending on your skin’s needs and age. If you want to focus on overall skin strength and appearance, choose type I collagen. If you need extra support for healing and repair, look for supplements with type iii collagen.
Tip: You can maximize your skin benefits by choosing hydrolyzed collagen peptides that include both type I and type iii collagen.
Medical Disclaimer: This information is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. You should consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Combined Use of Type I and Type III
Why Combine Both?
You can support your skin’s health by combining type I and type III collagen. Research shows that when you stimulate both types together, you help your skin maintain a better balance between strength and repair. For example, combining nutrients like ascorbic acid and glycinamide increases the production of both collagen types in your skin cells. This synergy helps you keep a healthy ratio of type III to type I collagen, which is important for skin elasticity, tension, and healing. As you age, this ratio drops, making your skin less firm and slower to heal. By using both types, you give your skin the building blocks it needs for structure and for recovery after damage. This approach can help you see better results in skin firmness, smoothness, and wound healing.
Tip: If you want to address both aging and skin repair, look for high-quality collagen supplements that include both type I and type III.
Bovine and Marine Collagen Sources
You have two main choices for high-quality collagen: bovine and marine sources. Each offers unique benefits for your skin.
Marine collagen comes from fish skin, scales, and bones. It contains mostly type I collagen. The peptides are smaller, so your body absorbs them quickly. Marine collagen is rich in glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline, which help your skin stay elastic and hydrated.
Bovine collagen comes from cow hides and bones. It provides both type I and type III collagen. The peptides are larger, but hydrolyzed bovine collagen breaks them down for better absorption. Bovine collagen also contains arginine, which supports your joints and gut as well as your skin.
Aspect | Marine Collagen | Bovine Collagen |
|---|---|---|
Source | Fish skin and scales | Cow hides and connective tissues |
Type of Collagen | Primarily Type I | Types I and III |
Amino Acids | High in glycine, proline, hydroxyproline | Rich in glycine, proline, hydroxyproline, arginine |
Bioavailability | Very high (smaller peptides) | High (slightly larger peptides) |
You may choose marine collagen for faster absorption or bovine collagen for a broader range of collagen types. Both can be part of a high-quality collagen routine.
Supplement Forms
You can find collagen supplements in several forms: powders, capsules, and liquids. All these forms contain hydrolyzed collagen peptides, which your body absorbs well. Clinical studies show that your body breaks down collagen into small peptides or amino acids before absorption, no matter the form. This means you get similar benefits from powders, capsules, or liquids.
Powders let you mix collagen into drinks or food and adjust your dose easily.
Capsules are convenient if you want a quick and simple option.
Liquids often come with flavors or extra ingredients for added benefits.
You should choose the form that fits your lifestyle and preferences. Daily use of any form, at doses between 2.5 and 15 grams, can help improve your skin’s hydration, elasticity, and smoothness over time.
Note: This information is for educational purposes only. It does not replace medical advice. Please consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Choosing Collagen Peptides
Assessing Skin Goals
You should start by identifying your main skin goals before choosing a collagen peptide product. Dermatologists recommend considering several factors to make the best choice:
Know your skin type. If you have oily, dry, or sensitive skin, you need a product that matches your hydration and support needs.
Identify your specific concerns. Look for issues like wrinkles, loss of firmness, redness, or slow healing.
Consider your age and lifestyle. Collagen production starts to decline in your mid to late 20s, so you may benefit from starting collagen peptide creams or supplements at this stage.
Check for complementary ingredients. Products with antioxidants, vitamins, or omega fatty acids can help brighten your skin and protect against free radicals.
Think about daily habits. Using collagen peptide creams with SPF during the day supports both defense and repair.
Tip: Assessing your goals helps you select a product that targets your unique needs and maximizes results.
Matching Collagen Type to Needs
You can match the type of collagen supplement to your skin needs by understanding the benefits of each type and the product’s source. Types I and III collagen are most important for skin health. Type I supports firmness and elasticity, while type III aids in repair and structure. Marine collagen, often sourced from fish skin, provides both types and absorbs quickly. Bovine collagen, from cow hides, also offers types I and III and supports a broader range of needs.
If you want to improve hydration and reduce wrinkles, look for supplements with types I and III collagen.
For faster absorption, marine collagen is a good choice.
If you prefer a product with added nutrients, choose one with vitamin C, zinc, or antioxidants to boost collagen synthesis and skin hydration.
Consistent use over 8-12 weeks helps you see visible improvements in texture, firmness, and tone. Combining collagen supplementation with a healthy diet, hydration, and sun protection gives you the best results.
Dosage and Safety
You should follow recommended dosages to ensure safe and effective results. Most clinical studies suggest taking 2.5 to 10 grams of hydrolyzed collagen peptides daily for 8-12 weeks. This range supports improved elasticity, hydration, and wrinkle reduction.
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Recommended Dosage | 2.5 to 10 grams daily of hydrolyzed collagen peptides |
Duration | 8-12 weeks |
Target Collagen Types | Type I and III (mainly found in skin) |
Benefits | Improved elasticity, hydration, and wrinkle reduction |
Safety Considerations | Generally safe; mild digestive discomfort possible |
Allergy Warnings | Avoid if allergic to fish, shellfish, or eggs |
Special Precautions | Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid due to limited safety data |
Recommendation | Consult a healthcare professional before starting supplementation |
Note: This information is for educational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice. You should consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
When to Consult a Professional
You may feel excited to try collagen supplements for your skin, but it is important to know when you should talk to a healthcare professional first. Collagen supplements can offer benefits, but they are not right for everyone. Your health and safety should always come first.
You should consult a doctor or registered dietitian before starting collagen supplementation. A professional can help you assess your individual health needs and recommend the right dosage for you. This step is especially important if you have any pre-existing medical conditions or health concerns. Your doctor can review your medical history and help you decide if collagen supplements are safe for you.
Some situations require extra caution. You should always speak with your doctor if you are:
Taking prescription medications or undergoing medical treatment
Living with chronic illnesses such as diabetes, kidney disease, or autoimmune disorders
Pregnant or breastfeeding
Recovering from surgery or a recent injury
Diagnosed with cancer or currently receiving cancer treatment
Collagen supplements are not regulated by the FDA. This means the quality and safety of these products can vary. Some supplements may contain toxins or heavy metals. You should look for products that have been tested by third-party organizations to ensure safety and purity. Your healthcare provider can help you choose a reputable brand.
If you have allergies to fish, shellfish, eggs, or beef, you need to be careful. Many collagen supplements come from animal sources. Your doctor can help you avoid products that might trigger an allergic reaction.
You may also want to consult a professional if you have concerns about possible side effects. Some people experience mild digestive discomfort when taking collagen. Your doctor can help you manage these symptoms or suggest alternatives.
Since the effectiveness of collagen supplements can be hard to track, a healthcare professional can help you set realistic expectations. They can discuss the potential risks and benefits with you. This guidance helps you make an informed decision about your skin health.
Note: The information in this article is for informational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice. You should always consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
Myths About Collagen
Common Misconceptions
You may see many claims about collagen in advertisements and social media. Some of these statements can mislead you. Dermatologists point out that media often exaggerates the benefits of collagen supplements for skin. You might hear that taking collagen will instantly make your skin glow or erase wrinkles. In reality, your body digests collagen supplements as food, not as direct building blocks for your skin. Collagen peptides do not travel straight to your skin to fill in gaps or boost radiance.
Many people believe marine collagen works better than animal collagen. Scientific studies show both types have similar effects when you take them as supplements. You may also see creams that promise to increase collagen in your skin. Collagen molecules are too large to pass through your skin’s outer layer, so these creams cannot reach the deeper dermis where collagen works.
Some think collagen supplements can reverse skin aging on their own. Your body’s collagen production slows down as you age, but you can stimulate it with active ingredients in creams or medical treatments like lasers. Collagen creams and supplements alone do not restore lost collagen. You need a holistic approach for best results.
Tip: Always check if a supplement has third-party lab verification. This helps you avoid contamination and incorrect dosing. Supplements from seafood sources may carry risks like heavy metal contamination, which can harm your organs.
Collagen supplements directly improve skin radiance and elasticity.
Marine collagen is more effective than animal collagen.
Collagen creams boost collagen levels deep in the skin.
Supplements alone can reverse skin aging.
What Science Says
You want to know what research says about collagen for skin health. Clinical studies show that hydrolyzed collagen peptides can improve skin hydration, elasticity, and firmness when you take them consistently for 8 to 12 weeks. You may notice fewer wrinkles and fine lines. Collagen supplements help stimulate fibroblasts, which are cells that produce collagen and support your skin’s structure.
You get the best results when you combine collagen supplements with a healthy lifestyle. Eating foods rich in vitamin C, protecting your skin from the sun, and avoiding smoking or high sugar intake all help your skin stay youthful. Collagen supplements work best as part of a complete skincare routine, not as a magic solution.
Collagen Benefit | How You Achieve It |
|---|---|
Hydration | Consistent supplementation |
Elasticity | Healthy diet, sun protection |
Firmness | Topical ingredients, lifestyle |
Wound Healing | Combined approach |
You should remember that the FDA does not approve dietary supplements for safety or effectiveness before they reach the market. Always choose products tested by third-party labs. Collagen supplements can support your skin from within, but you need to pair them with good habits and dermatological care.
Note: The information in this article is for informational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice. You should consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.
You gain the most skin strength and firmness from type I collagen, while type III collagen helps your skin stay elastic and supports repair. Both types work together to keep your skin healthy as you age. To choose the right supplement for your needs, follow these steps:
Identify your main skin goals, such as reducing wrinkles or boosting hydration.
Select type I for firmness or type III for elasticity and repair.
Choose hydrolyzed collagen for better absorption and look for added vitamin C.
This article is for informational purposes only. Please consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
FAQ
What is the difference between type I and type III collagen for skin?
Type I collagen gives your skin strength and firmness. Type III collagen helps with repair and elasticity. You need both for healthy, resilient skin. Most supplements combine these types for balanced benefits.
Can you take type I and type III collagen together?
Yes, you can take both types together. Many supplements contain a blend. You support your skin’s structure and repair by using both. This combination helps you see better results in hydration and elasticity.
How long does it take to see results from collagen peptides?
You usually notice improvements in skin hydration and elasticity after 8 to 12 weeks of daily use. Consistency matters. You should follow the recommended dosage for best results.
Are collagen supplements safe for everyone?
Most people tolerate collagen supplements well. Mild digestive discomfort may occur. You should avoid them if you have allergies to fish, shellfish, or beef. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult a doctor before use.
Which source is better: marine or bovine collagen?
Marine collagen absorbs quickly and contains mostly type I collagen. Bovine collagen provides both type I and type III. You should choose based on your skin goals and any allergies.
Do collagen creams work as well as supplements?
Collagen creams cannot reach deep skin layers. You get better results from oral supplements. Your body absorbs peptides and uses them to support collagen production from within.
Can you boost collagen naturally without supplements?
You support collagen production by eating foods rich in vitamin C, protein, and antioxidants. Protect your skin from sun damage. Healthy habits help your body make more collagen.
Medical Disclaimer:
The information in this FAQ is for informational purposes only. It does not constitute medical advice. You should consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.


