You may find magnesium glycinate works best for PMS cramps because it absorbs well, eases pain, and treats your stomach gently. Magnesium citrate also helps, especially if you deal with constipation, but it might cause mild digestive upset. Many people worry about magnesium supplementation causing high blood pressure or sugar spikes, but taking the best magnesium supplement at recommended doses is safe. Magnesium supports muscle relaxation and relieves period cramps. You deserve relief from PMS and premenstrual syndrome pain, so let’s explore practical ways to choose the right magnesium for your needs.
Key Takeaways
Magnesium glycinate absorbs well, calms muscles, and is gentle on the stomach, making it ideal for PMS cramps.
Magnesium citrate absorbs quickly and helps relieve constipation but may cause mild digestive upset like loose stools.
Both magnesium forms support muscle relaxation and reduce menstrual pain by lowering inflammation and balancing hormones.
Magnesium deficiency is common in women with PMS and can worsen cramps, mood swings, and fatigue.
Start magnesium supplements at a low dose (150-300 mg daily) and increase slowly to avoid side effects.
Choose magnesium glycinate if you have a sensitive stomach or want to ease anxiety and improve sleep.
Choose magnesium citrate if you need fast absorption and relief from constipation along with cramps.
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting magnesium supplements, especially if you have health conditions or take medications.
Comparison Overview
Key Differences
When you compare magnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate for PMS cramps, you notice some important differences. Both forms of magnesium help with muscle relaxation and cramp relief, but they work in slightly different ways. Magnesium glycinate stands out for its calming effects and gentle action on your stomach. Magnesium citrate, on the other hand, supports digestion and can help if you struggle with constipation during PMS.
Here is a quick table to help you see the main differences:
Feature | Magnesium Glycinate | Magnesium Citrate |
|---|---|---|
Absorption | Moderate to high, may cause mild GI upset | |
Affordability | More affordable | |
Tolerance | Well tolerated | Well tolerated, but may cause loose stools |
Availability | Easy to find in capsules, powders, liquids | Also widely available |
PMS Benefits | Best for PMS cramps, calming, supports hormones | Good for cramps, helps with constipation |
You usually find magnesium glycinate is preferred for PMS cramps because it absorbs well and rarely causes stomach problems. Magnesium citrate works well if you need extra digestive support.
Absorption
Your body absorbs magnesium in different ways depending on the form. Magnesium glycinate uses amino acid chelation, which means it attaches to glycine. This process helps your intestines take in more magnesium and reduces the chance of stomach upset. Clinical studies show that amino acid-chelated forms like magnesium glycinate have higher bioavailability and better tolerability than many other types.
Magnesium citrate also absorbs well, especially when you take it with food or liquid. However, it can be a bit less gentle on your stomach. Some people notice mild digestive effects, such as loose stools, because magnesium citrate draws water into your intestines. Both forms provide efficient magnesium supplementation, but magnesium glycinate often gives you better absorption with fewer side effects.
Side Effects
Most people tolerate both magnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate well. You might experience mild side effects like nausea, diarrhea, or stomach cramps, which are common with any magnesium supplement. Serious side effects rarely happen. Magnesium citrate may cause a laxative effect, especially if you take high doses. Magnesium glycinate usually feels gentler on your stomach and is less likely to cause digestive upset.
Clinical evidence shows that the side effect profiles for both forms are similar. No strong data proves that one causes more problems than the other, but you may find magnesium glycinate easier to tolerate if you have a sensitive stomach.
Note: Always talk to your healthcare provider before starting magnesium supplementation, especially if you have health conditions or take other medications.
Magnesium for PMS
Muscle Relaxation
You may notice your muscles feel tense and sore during PMS. Magnesium plays a key role in muscle relaxation and cramp relief. It controls calcium flow in your muscle cells, which helps your uterus relax and prevents painful contractions. When you take magnesium for PMS, you support your body’s ability to ease muscle tension and reduce cramps. Many women find that magnesium for period cramps works because it calms the muscles and lowers pain. This mineral also helps your body recover from muscle stress, which improves your overall menstrual health.
Tip: If you experience tight muscles or cramps before your period, magnesium can help you feel more comfortable and relaxed.
Menstrual Pain Relief
Magnesium offers relief from menstrual pain in several ways. It reduces inflammation, which lowers pain and swelling linked to premenstrual syndrome. Magnesium also helps balance hormones like estrogen and progesterone. This balancing hormones effect stabilizes your mood and reduces irritability. You may notice less anxiety and fewer mood swings when you use magnesium for PMS. Magnesium calms your nervous system by regulating neurotransmitters, which helps you feel less stressed and more at ease during your cycle.
Here are some ways magnesium supports menstrual health and pain relief:
Relaxes uterine muscles to reduce cramps
Lowers inflammation and pain
Supports hormonal balance for better mood
Calms nerves to ease anxiety
Boosts energy and reduces fatigue
Many women use magnesium for PMS because it helps with both physical and emotional symptoms. You may find topical magnesium works quickly to relieve cramps, breast tenderness, and sleep problems.
Deficiency Impact
Magnesium deficiency affects many women, especially during the premenstrual week. Low magnesium levels can make PMS symptoms worse, including cramps, pain, mood swings, and fatigue. Studies show that over half of women with hormone-related conditions have magnesium deficiency. This problem can lead to more severe menstrual health issues and less relief from PMS symptoms.
Population Group | Sample Size | Magnesium Deficiency Prevalence (serum Mg < 0.66 mmol/L) | Magnesium Deficiency Prevalence (serum Mg < 0.8 mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
Women with hormone-related conditions | 9444 | 21.4% | |
Subgroup: Women with PMS | 1549 | Included in HRC group | Included in HRC group |
If you struggle with PMS or premenstrual syndrome, checking your magnesium levels may help you find better relief. Supplementing with magnesium can reduce anxiety, mood swings, and pain. It also helps with bloating and swelling by acting as a natural diuretic.
Medical Disclaimer: This blog provides general information about magnesium and menstrual health. You should consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplement, especially if you have medical conditions or take other medications.
Magnesium Glycinate Benefits
Absorption
You want a magnesium supplement that your body can absorb easily. Magnesium glycinate stands out because it binds magnesium to glycine, an amino acid. This form helps your body take in more magnesium with less waste. Mouse model studies show that magnesium glycinate increases blood magnesium levels more effectively than many other forms. While some research in animals suggests other forms like magnesium citrate may boost tissue magnesium in certain areas, magnesium glycinate remains a top choice for raising overall magnesium levels in your body. Many health professionals recommend magnesium glycinate as the best magnesium supplement for people who need to improve their magnesium status. You can trust this form to deliver reliable results, even if direct human absorption studies are still limited.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Magnesium glycinate does more than just raise your magnesium levels. It also helps your body fight inflammation, which plays a big role in PMS cramps and menstrual pain. Clinical studies show that magnesium supplements, including magnesium glycinate, lower inflammation markers like C-reactive protein and interleukin-6. These markers rise when your body faces stress or pain, especially during your period. If you have low magnesium, you may notice more swelling, pain, and discomfort. By taking magnesium glycinate, you help your body control these symptoms. Many experts recommend magnesium glycinate for menstrual pain because it works well and causes fewer stomach problems than other forms. Some guidelines suggest using up to 600 mg daily for the best results, especially when combined with vitamin B6. You may find that magnesium glycinate is the best magnesium supplement for easing cramps and reducing inflammation during PMS.
Gentle on Digestion
If you have a sensitive stomach, you want a magnesium supplement that will not upset your digestion. Magnesium glycinate is known for being gentle. Unlike magnesium citrate, which often acts as a laxative and can cause diarrhea or stomach cramps, magnesium glycinate rarely causes these problems. Clinical trials show that magnesium glycinate does not draw water into your intestines, so you avoid the sudden urge to use the bathroom. This makes it a great option if you want to boost your magnesium without digestive side effects. People who struggle with stomach issues or want to avoid laxative effects often choose magnesium glycinate as their best magnesium supplement. You can take it daily with confidence, knowing it supports your health without causing discomfort.
Medical Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only. Always talk to your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have health conditions or take medications.
Best for PMS Cramps
You want real relief from PMS cramps, not just a temporary fix. Magnesium glycinate stands out as the best magnesium supplement for this purpose. Many women choose magnesium glycinate because it combines high absorption with a gentle effect on your stomach. You get the benefits of magnesium without the digestive upset that some other forms can cause.
Magnesium glycinate works in several ways to help you manage PMS cramps:
It relaxes your uterine muscles, which helps reduce the intensity and frequency of cramps.
It lowers inflammation, so you feel less pain and swelling during your period.
It supports hormone balance, which can ease mood swings and irritability.
You may notice that magnesium glycinate helps you feel calmer and more comfortable during your cycle. This form of magnesium binds to glycine, an amino acid that also has calming effects on your nervous system. You get a double benefit: muscle relaxation and stress relief. Many health experts recommend magnesium glycinate as the best magnesium supplement for PMS cramps because it addresses both physical and emotional symptoms.
If you have tried other forms of magnesium and experienced side effects like diarrhea or stomach cramps, magnesium glycinate offers a better option. You can take it daily without worrying about sudden trips to the bathroom. This makes it easier to stick with your supplement routine and see real results over time.
Here are some reasons why magnesium glycinate is often considered the best magnesium supplement for PMS cramps:
Benefit | Why It Matters for PMS Cramps |
|---|---|
High absorption | More magnesium reaches your muscles |
Gentle on digestion | Less risk of stomach upset |
Calming effect | Reduces stress and anxiety |
Anti-inflammatory properties | Less pain and swelling |
Supports hormone balance | Fewer mood swings and irritability |
Tip: Start taking magnesium glycinate a week before your period begins. This can help prevent cramps before they start and make your cycle more manageable.
You deserve to feel your best every month. Magnesium glycinate gives you a safe, effective way to manage PMS cramps and improve your overall well-being. If you want the best magnesium supplement for period pain, magnesium glycinate is a top choice.
Medical Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only. Always talk to your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have health conditions or take medications.
Magnesium Citrate Benefits
Absorption
You may wonder how well your body absorbs magnesium citrate compared to other forms. Magnesium citrate stands out for its high bioavailability. When you take magnesium citrate, your body absorbs it more efficiently than inorganic forms like magnesium oxide. Studies show that magnesium citrate leads to higher urinary magnesium excretion and increased serum magnesium concentrations within hours after you take it. This means more magnesium reaches your bloodstream, supporting muscle function and overall health.
Parameter | Magnesium Citrate (Organic) | Magnesium Oxide (Inorganic) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Urinary Magnesium Excretion (Ae 0-24h) | Higher (0.565 mmol difference) | Lower | Magnesium citrate absorbs better (p = 0.0034) |
Serum Magnesium Concentrations | Higher at 2-6 hours post-dose | Lower | Significant differences (p < 0.004) |
Intracellular Magnesium Levels | No significant difference | No significant difference | Not reliable for single-dose absorption assessment |
General Conclusion | Superior bioavailability | Less absorbable | Organic magnesium compounds like citrate work best |
Magnesium citrate gives you a reliable way to boost your magnesium levels quickly. You can trust this form to deliver results, especially if you need fast support for PMS cramps.
Digestive Support
Magnesium citrate offers unique digestive benefits. If you struggle with constipation during PMS, magnesium citrate helps maintain regular bowel movements. It relaxes your bowels and draws water into your intestines, making stool passage easier. Many people use magnesium citrate as a supplement to relieve occasional constipation. You should follow dosage instructions carefully to avoid unwanted effects.
Magnesium citrate supports normal bowel movements by relaxing the bowels.
It draws water into the intestines, which softens stools.
You can use it for occasional constipation relief.
Good hydration, a balanced diet, and exercise also help digestive health.
Magnesium citrate supplements with high bioavailability work best.
Magnesium citrate absorbs easily in your intestines. It increases water absorption in the small intestine and enhances muscle contractions, known as peristalsis. This process promotes regular bowel movements. Gastroenterologists recommend magnesium citrate as a safe and effective option for constipation, including cases caused by medications. You can find magnesium citrate widely available in stores and online.
Tip: If you experience constipation along with PMS cramps, magnesium citrate may offer the digestive support you need.
Laxative Effect
Magnesium citrate acts as a fast-acting osmotic laxative. After you take it, you may notice bowel movements within 30 minutes to 6 hours. Magnesium citrate draws water into your intestines, softening stools and making them easier to pass. This mechanism explains why laxative effects, such as diarrhea, are common and expected side effects.
Studies show that gastrointestinal side effects occur in about 10% to 30% of people who use magnesium citrate for muscle cramps, including PMS cramps. The severity and onset of these effects depend on your metabolism, hydration, and how closely you follow dosage instructions.
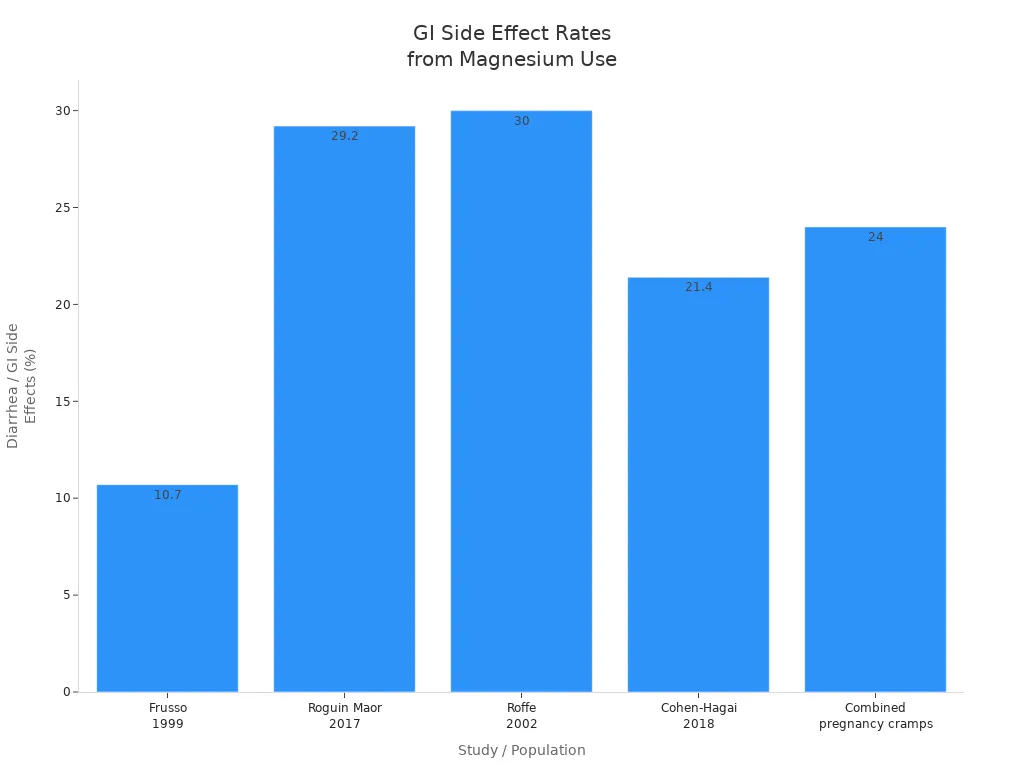
You should anticipate the possibility of diarrhea or loose stools when using magnesium citrate for PMS cramps. If you have a sensitive stomach or want to avoid laxative effects, you may prefer other forms of magnesium.
Note: Always consult your healthcare provider before starting magnesium citrate, especially if you have digestive concerns or take other medications.
Medical Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only. You should talk to your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement.
When to Choose Citrate
You may wonder when magnesium citrate is the right choice for PMS cramps. This form of magnesium works best for certain situations and symptoms. Understanding your needs helps you decide if magnesium citrate fits your lifestyle.
Choose magnesium citrate if you:
Experience constipation along with PMS cramps. Magnesium citrate acts as a gentle laxative and helps keep your bowels regular.
Prefer a supplement that absorbs quickly. Magnesium citrate enters your system fast and raises your magnesium levels efficiently.
Want a widely available and affordable option. You can find magnesium citrate in most pharmacies and health stores.
Do not have a sensitive stomach. Some people notice mild digestive side effects, but many tolerate magnesium citrate well.
Magnesium citrate supports your digestive health while easing muscle cramps. If you often feel bloated or have trouble with bowel movements during your period, this form of magnesium may give you double benefits. You get relief from cramps and support for regular digestion.
Tip: Take magnesium citrate with a full glass of water. This helps your body absorb the supplement and reduces the risk of stomach upset.
Here is a quick comparison to help you decide:
Situation | Is Magnesium Citrate a Good Choice? |
|---|---|
PMS cramps with constipation | ✅ Yes |
Sensitive stomach | ❌ No (consider glycinate) |
Need fast absorption | ✅ Yes |
Want to avoid laxative effect | ❌ No |
Looking for affordable option | ✅ Yes |
You should avoid magnesium citrate if you have chronic diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome, or a very sensitive digestive system. In these cases, magnesium glycinate may suit you better. Always start with a low dose and see how your body reacts.
Magnesium citrate offers a practical solution for people who need both cramp relief and digestive support. If you want a supplement that works quickly and helps with constipation, magnesium citrate stands out as a smart choice.
Medical Disclaimer: This information is for educational purposes only. You should consult your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have health conditions or take medications.
Period Cramps: Which Magnesium Is Better?
Effectiveness
You want the best magnesium supplement to manage period cramps. Magnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate both help reduce pain and muscle tension. Magnesium glycinate absorbs quickly and delivers magnesium directly to your muscles. This form helps relax your uterus and lowers the intensity of cramps. Many people find magnesium glycinate works well for PMS and period cramps because it calms nerves and supports hormone balance.
Magnesium citrate also provides strong support for menstrual health. It absorbs efficiently and raises magnesium levels in your blood. If you need fast results, magnesium citrate can help ease cramps and pain. You may notice relief within a few hours after taking it. Magnesium citrate works especially well if you experience constipation along with period cramps.
Here is a quick comparison to help you decide:
Magnesium Form | Absorption Speed | Muscle Relaxation | Hormone Support | Constipation Relief |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Magnesium Glycinate | Fast | Excellent | Yes | No |
Magnesium Citrate | Fast | Good | Yes | Yes |
Both forms of magnesium for period cramps offer effective pain relief. Magnesium glycinate stands out for its calming effects and gentle action. Magnesium citrate works best if you need digestive support along with cramp relief.
Tolerability
You want a magnesium supplement that feels comfortable and easy to take. Magnesium glycinate is well tolerated by most people. You rarely experience digestive upset or diarrhea with this form. Magnesium glycinate is gentle on your stomach and does not cause sudden bowel movements. You can take it daily without worrying about discomfort.
Magnesium citrate is also well absorbed, but it may cause mild gastrointestinal side effects. You might notice loose stools or mild stomach cramps, especially if you take high doses. Magnesium citrate acts as a gentle laxative, which helps if you struggle with constipation during PMS. If you have a sensitive digestive system, you should start with a low dose and see how your body reacts.
Tip: If you want to avoid digestive side effects, magnesium glycinate is usually the better choice for period cramps.
Sensitive Stomachs
If you have a sensitive stomach, choosing the right magnesium supplement is important for your menstrual health. Clinical evidence shows that magnesium glycinate is gentle on digestion and causes minimal gastrointestinal side effects. You are less likely to experience diarrhea or stomach upset with magnesium glycinate. This makes it a preferred option for people with sensitive digestion or a history of GI issues.
Magnesium citrate, while effective, can cause mild laxative effects due to its osmotic activity in the gut. You may feel discomfort or experience loose stools if your stomach is sensitive. Clinical studies confirm that magnesium citrate’s high bioavailability comes with a risk of GI side effects. If you have a sensitive stomach, you should consider magnesium glycinate instead. Always consult your healthcare provider to determine the best magnesium supplement and the right dose for your needs.
Note: Large or frequent doses of any magnesium supplement can cause nausea, abdominal cramps, or diarrhea. Start with a low dose and increase slowly to avoid digestive problems.
Medical Disclaimer:
This blog provides general information about magnesium supplements and menstrual health. You should talk to your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have medical conditions or take medications.
Choosing Magnesium for PMS
Matching Symptoms
You can match your magnesium supplement to your PMS symptoms for better results. Many women experience cramps, mood swings, fatigue, and digestive changes during premenstrual syndrome. Magnesium glycinate works well if you feel anxious, have trouble sleeping, or want to support hormonal balance. This form helps calm your nervous system and improves sleep quality. Magnesium citrate is a good choice if you struggle with constipation or digestive discomfort during PMS. It absorbs quickly and helps relieve pain from cramps, but may cause loose stools.
Clinical studies suggest that magnesium supplementation at about 250 mg daily may help with PMS symptoms, especially when combined with vitamin B6. Although more research is needed, low magnesium levels often appear in women with PMS. You may notice symptoms like fatigue, weakness, cramps, nausea, or loss of appetite. These signs can mean your body needs more magnesium for PMS relief.
Symptom | Best Magnesium Form | Why Choose This Form |
|---|---|---|
Anxiety, mood swings | Magnesium glycinate | Calms nerves, supports balancing hormones |
Sleep problems | Magnesium glycinate | Improves sleep onset and quality |
Muscle cramps | Magnesium citrate | Fast absorption, helps relieve pain |
Constipation | Magnesium citrate | Gentle laxative effect, supports digestion |
Sensitive digestion | Magnesium glycinate | Less likely to cause stomach upset |
Tip: If you notice bloating, fluid retention, or breast tenderness, magnesium supplementation may help reduce these PMS symptoms.
Lifestyle Factors
Your lifestyle can guide your choice between magnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate. If you eat a magnesium-rich diet and stay active, you may need a supplement that supports relaxation and sleep. Magnesium glycinate fits this need because it absorbs well and calms your body. If you have a busy schedule, experience stress, or eat foods low in magnesium, you might benefit from magnesium citrate. This form helps with digestive issues and provides rapid magnesium delivery.
Physical activity and diet affect your digestive health and symptom profile. Magnesium glycinate is less likely to cause digestive upset, making it suitable for sensitive stomachs. Magnesium citrate works best for women who need help with constipation or want quick relief from cramps.
Lifestyle Factor | Magnesium Glycinate | Magnesium Citrate |
|---|---|---|
Highly absorbed, gentle | Well absorbed, fast acting | |
Digestive impact | Minimal, calming | Laxative effect, may cause loose stools |
Recommended for | Sensitive digestion, stress | Constipation, rapid relief |
Diet considerations | Complements magnesium-rich diet | Supports digestion, useful with low magnesium intake |
Note: Your daily habits, diet, and physical activity level can help you decide which magnesium supplement fits your menstrual health needs.
Healthcare Advice
You should always consult a healthcare provider before starting magnesium supplementation for PMS. Healthcare professionals recommend magnesium glycinate for women with sensitive digestion or those seeking hormonal balance and relaxation. You can take magnesium glycinate in the evening to support sleep and reduce pain. Magnesium citrate is effective for muscle cramps and digestive sluggishness, but it may cause mild laxative effects. If you do not have digestive sensitivity, you can use magnesium citrate earlier in the day for cramp relief.
Magnesium glycinate is gentle on your stomach and supports balancing hormones.
Magnesium citrate absorbs quickly and helps with cramps and constipation.
Both forms can be used strategically based on your symptoms and daily routine.
Medical Disclaimer: This blog provides general information about magnesium supplementation and menstrual health. You should talk to your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have medical conditions or take medications.
Dosage and Safety
Recommended Dosage
You want to get the most benefit from magnesium while keeping side effects low. Most studies suggest starting with a daily dose between 150 mg and 300 mg for PMS cramps. This range works well for many people and helps reduce pain and muscle tension. The typical dosage for magnesium glycinate is 200 mg to 300 mg per day, which offers high absorption and gentle effects on your stomach. If you choose magnesium citrate, a common dosage for magnesium citrate is 150 mg to 300 mg per day. Always check the label for the exact amount of elemental magnesium in your supplement.
Tip: Start with the lowest effective dose. You can increase slowly if you do not notice relief after a week or two.
Safe Use
Magnesium is generally safe for most people, but you should follow some important safety steps:
Consult your healthcare provider before starting magnesium supplementation, especially if you have health problems or take other medications.
Begin with a low dose, such as 150 mg per day, to see how your body reacts.
Watch for mild side effects like diarrhea, nausea, or stomach upset. These effects are more common with higher doses or certain forms.
Choose high-quality supplements that have third-party testing for purity and accurate labeling.
If you have sensitive digestion, magnesium glycinate is often easier to tolerate.
Avoid magnesium supplements if you have kidney disease or severe renal impairment. High magnesium levels can cause serious health problems, including heart rhythm changes and muscle weakness.
Some drugs interact with magnesium, such as certain antibiotics, diuretics, and muscle relaxants. Take magnesium at a different time than these medications, or ask your doctor for advice.
⚠️ Medical Disclaimer: Always talk to your healthcare professional before starting magnesium supplements or changing your health routine. This is especially important if you have kidney problems, take prescription drugs, or have other health concerns.
Adjusting Dose
You may need to adjust your magnesium dose based on your symptoms and how your body responds. If you notice side effects like loose stools or stomach cramps, lower your dose or switch to a different form. Track your symptoms in a journal to see if magnesium helps with PMS cramps, mood swings, or sleep. If you do not feel better after a few weeks, talk to your healthcare provider about changing your dosage or trying another type of magnesium.
Increase your dose slowly if you do not get relief, but do not exceed the recommended maximum unless your doctor says it is safe.
Combine magnesium with other remedies, such as heat packs or over-the-counter pain relief, for better results.
Stop taking magnesium and seek medical help if you notice serious symptoms like muscle weakness, irregular heartbeat, or trouble breathing.
A careful approach to magnesium supplementation helps you find the right balance between relief and safety.
You often find magnesium glycinate works best for PMS and period cramps. This form absorbs well, supports muscle relaxation, and rarely causes stomach upset. The glycine in magnesium glycinate also helps with mood and hormonal balance. If you struggle with constipation during premenstrual syndrome, magnesium citrate may suit you. It absorbs quickly and relieves cramps, but sometimes causes digestive side effects.
Magnesium Form | Best For | Digestive Impact |
|---|---|---|
Magnesium Glycinate | PMS cramps, sensitive stomach | Gentle |
Magnesium Citrate | PMS with constipation | Possible loose stools |
Always talk to your healthcare provider before starting magnesium supplements. With the right choice, you can find real relief from PMS cramps.
FAQ
Can magnesium help with PMS cramps?
You can use magnesium to relax your muscles and reduce PMS cramps. Magnesium supports hormone balance and lowers inflammation. Many women find relief from period pain with regular magnesium supplementation.
Which magnesium form is best for sensitive stomachs?
You may prefer magnesium glycinate if you have a sensitive stomach. This form absorbs well and rarely causes digestive upset. Magnesium citrate may cause loose stools or mild discomfort.
How long does it take for magnesium to work on PMS cramps?
You may notice improvement in PMS cramps within a few days to two weeks after starting magnesium. Consistent daily use gives the best results. Track your symptoms to see changes.
Can I take magnesium for leg cramps during PMS?
You can use magnesium supplements to help with leg cramps that occur during PMS. Magnesium supports muscle relaxation and may reduce cramping in your legs and uterus.
Is it safe to take magnesium every day?
You can safely take magnesium daily at recommended doses. Most people tolerate 150 mg to 300 mg per day. Always check with your healthcare provider before starting any supplement.
What are common side effects of magnesium supplements?
You may experience mild side effects like diarrhea, nausea, or stomach cramps. Magnesium citrate may cause loose stools. Magnesium glycinate is gentler on digestion.
Should I take magnesium with food or on an empty stomach?
You can take magnesium with food to improve absorption and reduce stomach upset. Some people tolerate magnesium well on an empty stomach, but food usually helps.
Medical Disclaimer
This FAQ provides general information about magnesium and PMS cramps. You should consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplement, especially if you have health conditions or take medications.


